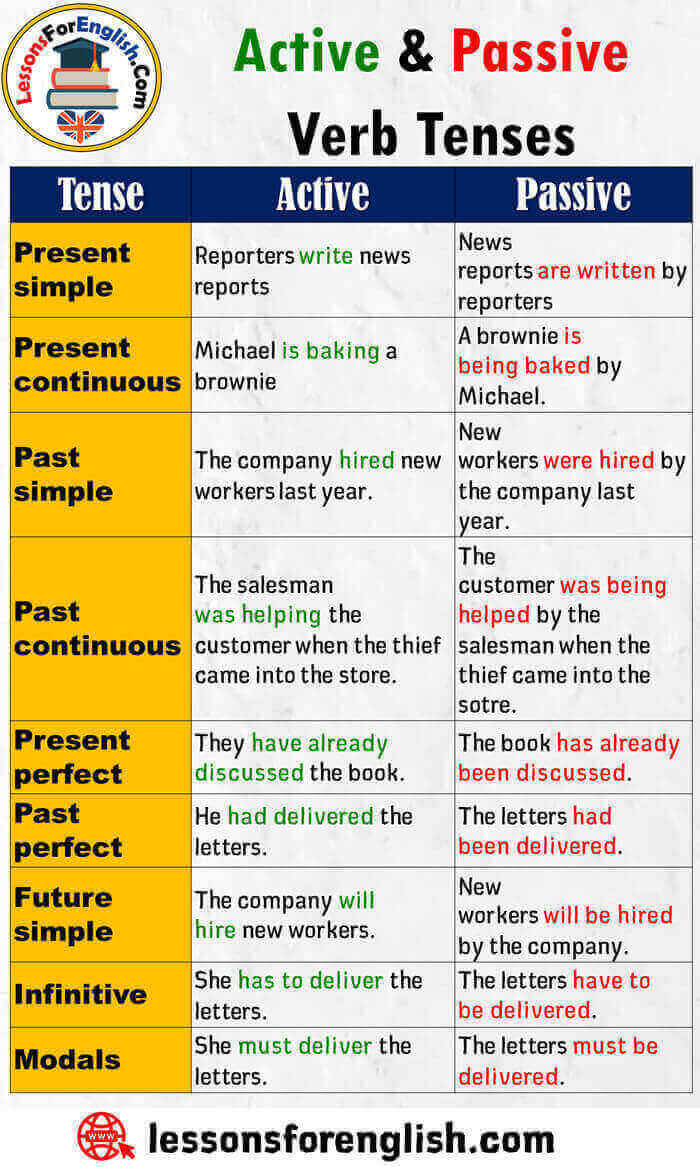
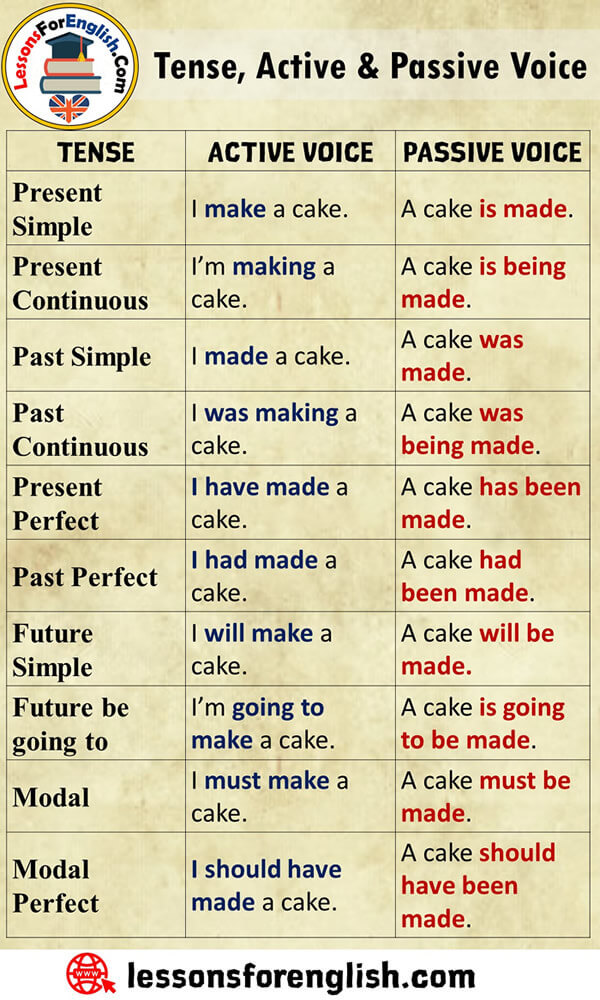
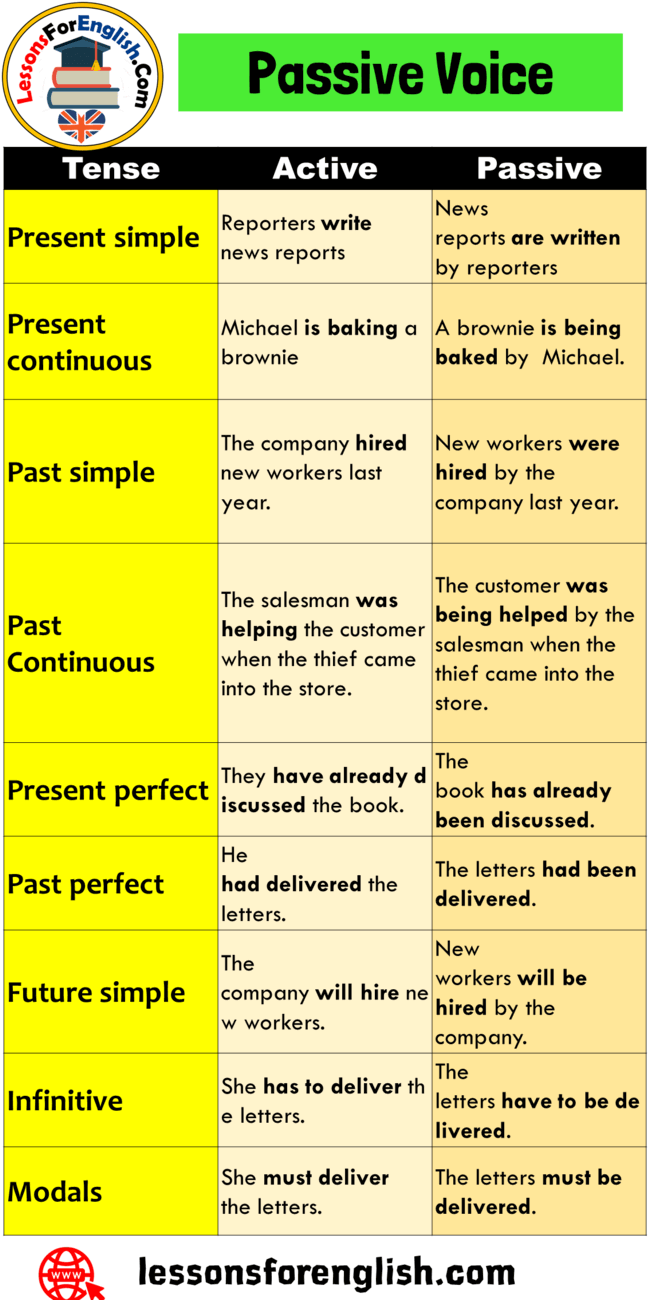
Active and Passive Voice in English

- An active clause refers to the action done on the object, but a passive clause indicates that the action is done by someone.
- We can change an active clause to passive, but for this, the active clause must be a transitive verb that can take an object such as open, close, give, buy, etc. Intransitive verbs do not take objects.
- Passive verbs cannot be passive forms.
Examples
The Simple Present (Active à Passive)
He washes the black car. à The black car is washed by him.
Present Continuous (Active à Passive)
He is washing the black car. / The black car is being washed by him.
Simple Past (Active à Passive)
He washed the black car. / The black car was washed by him.
Past Continuous (Active à Passive)
He was washing the black car. / The black car was being washed by him.
Present Perfect (Active à Passive)
He has washed the black car. / The black car has been washed by him.
Past Perfect (Active à Passive)
He had washed the black car. / The black car had been washed by him.
Going to future (Active à Passive)
He is going to wash the black car. / The black car is going to be washed by him.
Future (Active à Passive)
He will have washed the black car. / The black car will have been washed by him.